With millions of new cases diagnosed each worldwide, prostate cancer ranks among the most frequent tumors affecting men. Prostate removal, also known as prostatectomy, is often required as a treatment option when the cancer is confined and has not spread beyond the prostate gland.
Open surgery, which involved making a big incision in the belly, was the usual method for performing prostatectomy. But surgical methods have come a long way in the previous several decades, especially with the advent of less intrusive procedures like robotic-assisted and laparoscopic surgeries.
Urology’s Increasing Use of Robotic Surgery
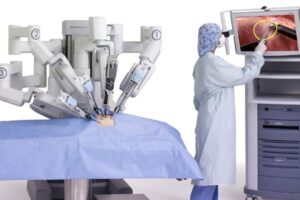
With the advent of cirugía robótica, urologists now have a less intrusive and more accurate method to remove the prostate. The da Vinci Surgical System, which has been around since the beginning of the 2000s, is a popular robotic system that is utilized for prostatectomy.
Compared to traditional open surgery, which requires huge incisions, this technique lets surgeons to work with more precision, flexibility, and control through the use of small incisions. One reason robotic-assisted surgery is becoming more popular is the hope that technology would helppatients have better results with less risk of problems and faster recoveries.
Methods for Performing a Robotic-Assisted Prostatectomy
As part of robotic-assisted prostatectomy, a laparoscopic procedure, the surgeon operates robotic arms stocked with surgical instruments via a control console. The device reduces the margin of error by translating the surgeon’s hand movements into accurate micro-movements. Here are the main steps of the process:
- Getting Ready: The surgical team gets the operating room ready as the patient is put under general anesthesia. A high-definition 3D camera and robotic arms are introduced through small incisions made in the belly.
- Removal of the Prostate: Surgeons use robotic arms and a control panel to remove the prostate gland and any surrounding tissues or lymph nodes with precision. Accurate dissection with little harm to adjacent structures, including the nerves regulating urination and libido, is made possible by the high-definition camera’s magnified, three-dimensional image of the surgical site.
- Reinstatement: Surgeons repair the urinary tract by connecting the bladder to the urethra after prostate removal. The patient’s capacity to urinate regularly following surgery depends on this phase.
Why Robotic Surgery Is Beneficial
Compared to open surgery and even regular laparoscopic treatments, robotic-assisted prostatectomy has various benefits:
- Robotic Surgery: Less invasive than open surgery because it uses smaller incisions, which means less blood loss, less postoperative pain, and less infection risk.
- Accuracy: To preserve sexual and urinary functioning, it may be essential to remove the prostate with precision while limiting harm to surrounding tissues; this is made possible by the robotic system’s improved control and visibility.
- Speedier Recovery: Robotic surgery patients typically have shorter hospital stays and get back to their daily routines faster. Postoperative comfort is enhanced by the fact that smaller incisions are connected with less pain and suffering.
- Better Results: Research has demonstrated that robotic-assisted prostatectomy can enhance long-term cancer control and reduce the occurrence of positive surgical margins, which indicate that cancer is still present at the tissue’s edge after removal.
The Prospects for Robotic Prostate Surgery
Aiming to improve patient outcomes and increase the applications of robotic systems, the field of robotic surgery is constantly evolving. More advanced robotic technology may be available in the future, allowing for more precise prostate removal surgeries with fewer complications.
Costs for robotic surgery may go down as training programs grow and robotic devices get more accessible, opening the door to this cutting-edge treatment option for more patients.
Conclusion
Finally, patients undergoing prostate cancer therapy now have a minimally invasive option thanks to robotic-assisted prostatectomy. This procedure has the ability to enhance outcomes and speed up recovery time. Robotic surgery is expanding its use in urology and other surgical specialties as a result of technological advancements, which bodes well for the future of patient care and the effectiveness of treatments.